一 概念
固定窗口就像是滑动窗口的一个特例,固定窗口是大小固定且不能随着时间而变化的。
滑动时间窗口就是把一段时间片分为多个样本窗口,可以通过更细粒度对数据进行统计。然后计算对应的时间落在那个窗口上,来对数据统计;滑动时间窗口,随着时间流失,最开始的样本窗口将会失效,同时会生成新的样本窗口。
例如 我们将1s划分为4个样本窗口,每个样本窗口对应250ms。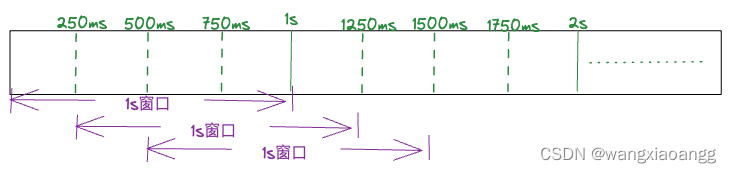
二 go-zero中的滑动窗口实现
1.bucket 样本窗口
bucket用于记录每个样本窗口的值
// bucket defines the bucket that holds sum and num of additions.
type bucket struct {
sum float64 //样本窗口的值
count int64 //样本窗口被add的次数
}
func (b *bucket) add(v float64) {
b.sum = v
b.count
}
//重置样本窗口,样本窗口过期时
func (b *bucket) reset() {
b.sum = 0
b.count = 0
}
2. window 滑动窗口
type window struct {
buckets []*bucket //样本窗口
size int //样本窗口个数
}
func newwindow(size int) *window {
buckets := make([]*bucket, size)
for i := 0; i < size; i {
buckets[i] = new(bucket)
}
return &window{
buckets: buckets,
size: size,
}
}
func (w *window) add(offset int, v float64) {
w.buckets[offset%w.size].add(v)
}
func (w *window) reduce(start, count int, fn func(b *bucket)) {
for i := 0; i < count; i {
fn(w.buckets[(start i)%w.size])
}
}
func (w *window) resetbucket(offset int) {
w.buckets[offset%w.size].reset()
}
3. rollingwindow窗口
bucket和window的实现都很简单,逻辑很好理解。
rollingwindow相对复杂一些。
当add值时需要如下操作:
- 计算已经过期的bucket(样本窗口),将已经过期的bucket重置。
- 计算offset,当前add操作应当记录到哪个bucket中。
type (
// rollingwindowoption let callers customize the rollingwindow.
rollingwindowoption func(rollingwindow *rollingwindow)
// rollingwindow defines a rolling window to calculate the events in buckets with time interval.
rollingwindow struct {
lock sync.rwmutex
size int
win *window
interval time.duration
offset int
ignorecurrent bool
lasttime time.duration // start time of the last bucket
}
)
// newrollingwindow returns a rollingwindow that with size buckets and time interval,
// use opts to customize the rollingwindow.
func newrollingwindow(size int, interval time.duration, opts ...rollingwindowoption) *rollingwindow {
if size < 1 {
panic("size must be greater than 0")
}
w := &rollingwindow{
size: size,
win: newwindow(size),
interval: interval,
lasttime: timex.now(),
}
for _, opt := range opts {
opt(w)
}
return w
}
// add adds value to current bucket.
func (rw *rollingwindow) add(v float64) {
rw.lock.lock()
defer rw.lock.unlock()
rw.updateoffset()
rw.win.add(rw.offset, v)
}
// reduce runs fn on all buckets, ignore current bucket if ignorecurrent was set.
func (rw *rollingwindow) reduce(fn func(b *bucket)) {
rw.lock.rlock()
defer rw.lock.runlock()
var diff int
//获取跨度,并计算还有几个bucket还在窗口期内
span := rw.span()
// ignore current bucket, because of partial data
if span == 0 && rw.ignorecurrent {
diff = rw.size - 1
} else {
diff = rw.size - span
}
if diff > 0 {
offset := (rw.offset span 1) % rw.size
rw.win.reduce(offset, diff, fn)
}
}
//距离上次add操作跨度,
//例如 lasttime = 1s, 当前时间1777ms。样本窗口时间250ms,那么跨度为3个样本窗口
func (rw *rollingwindow) span() int {
offset := int(timex.since(rw.lasttime) / rw.interval)
if 0 <= offset && offset < rw.size {
return offset
}
return rw.size
}
//g
func (rw *rollingwindow) updateoffset() {
span := rw.span()
if span <= 0 {
return
}
offset := rw.offset
// reset expired buckets ,重置已经超时的bucket
for i := 0; i < span; i {
rw.win.resetbucket((offset i 1) % rw.size)
}
rw.offset = (offset span) % rw.size
now := timex.now()
//和样本窗口时间对齐
rw.lasttime = now - (now-rw.lasttime)%rw.interval
}三 使用
//1.新建一个4样本窗口,每个样本窗口250ms
rollingwindow:= newrollingwindow(4, time.millisecond*250,ignorecurrentbucket())
//2.add
rollingwindow.add(1)
rollingwindow.add(2)
time.sleep(time.millisecond*250)
rollingwindow.add(3)
rollingwindow.add(4)
//3.获取滑动窗口的值
var sum float64
var total int64
rollingwindow.reduce(func(b *collection.bucket) {
sum = int64(b.sum)
total = b.count
})